Black-Scholes Calculator with Dividend Yield
The original Black-Scholes option pricing model (Black, Scholes, 1973) assumes that the underlying security does not pay any dividends. In other words, dividends don't enter option price calculation in any way.
The Black-Scholes Calculator uses the expanded version of the model (Merton, 1973) that can price options on securities that pay a dividend. The calculation assumes that the underlying security pays a continuous dividend at the rate you set as entry parameter.
Entering Dividend Yield as Parameter in Black-Scholes Calculator
Enter the continuous dividend yield, in percent per annum (% p.a.) in the yellow cell C12 in the sheet "Pricing".
Dividend Yield Effects on Option Prices and Greeks
Dividend yield usually doesn't change as quickly and as much as some of the other parameters (like volatility or underlying price), but if you need you can also simulate effects of dividend yield changes on option prices and Greeks.
Select "Dividend Yield" in the dropdown box in cell C27.
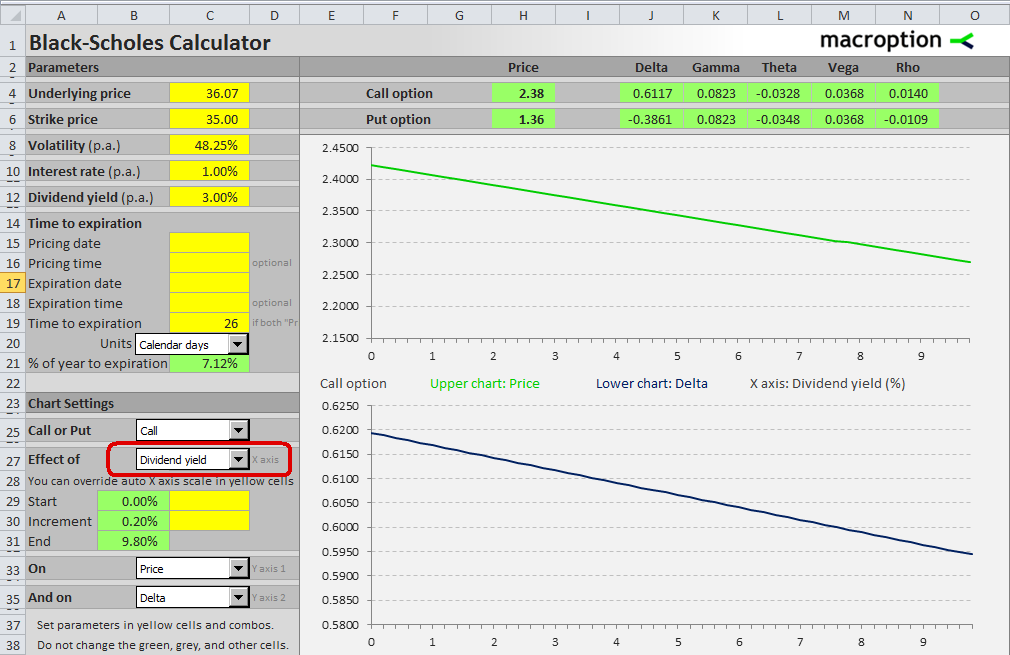
The charts on the screenshot above show the impact of dividend yield (X axis) on a call option's price (upper Y axis) and delta (lower Y axis), for a set of parameters you set in the top left corner – in this case underlying price 36.07, strike price 35, volatility 48.25%, interest rate 1%, and 26 calendar days to expiration.
Alternatively, you can set the charts to display the effect of another input parameter (for example underlying price or volatility) and then see how the charts change if you set different dividend yield values in cell C12. You can find more detailed explanation of simulations and charts in chapter 7 of the user guide that comes with the spreadsheet.
Black-Scholes Calculator without Dividend Yield
If you want the exact original Black-Scholes model (without dividends), just set dividend yield in cell C12 to zero.
More Information and Download
Here you can see more information about the functions and features of the Black-Scholes Calculator.